Cancer
Blog Title
3935 |
According to a study published Online First by The Lancet, breast, cervical and stomach cancers are responsible for the majority of cancer deaths among women in India, while lung, oral and stomach cancers are the leading causes of cancer death in Indian men.
The number of oral cancers is more than twice the number of lung cancers in individuals aged 30-69 years.
Causes and Prevention:
At least one-third of all cancer casesarepreventable. Prevention offers the most cost-effective long-term strategy for the control of cancer.
Tobacco
Tobacco use is the single greatest avoidable risk factor for cancer mortality worldwide, causing an estimated 22% of cancer deaths per year. In 2004, 1.6 million of the 7.4 million cancer deaths were due to tobacco use.
Tobacco smoking causes many types of cancer, including cancers of the lung, oesophagus, larynx (voice box), mouth, throat, kidney, bladder, pancreas, stomach, and cervix. About 70% of the lung cancer burden can be attributed to smoking alone. Second-hand smoke (SHS), also known as environmental tobacco smoke, has been proven to cause lung cancer in non-smoking adults. Smokeless tobacco (also called oral tobacco, chewing tobacco or snuff) causes oral and pancreatic cancer.
Physical inactivity, dietary factors, obesity and being overweight
Dietary modification is another important approach to cancer control. There is a link between being overweight as well as obesity to many types of cancer such as oesophagus, colorectal, breast, endometrium and kidney. Diets high in fruits and vegetables may have a protective effect against many cancers. Conversely, excess consumption of red and preserved meat may be associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer. In addition, healthy eating habits that prevent the development ofdiet associated cancers will also lower the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Regular physical activity and the maintenance of a healthy body weight, along with a healthy diet, will considerably reduce cancer risk.
Alcohol use
Alcohol use is a risk factor for many cancer types including cancer of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, oesophagus, liver, and breast. The risk of cancer increases with the amount of alcohol consumed. The risk from heavy drinking for several cancer types (e.g. oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, and oesophagus) substantially increases if the person is also a heavy smoker.
Infections
Infectious agents are responsible for almost 22% of cancer deaths in the developing world and 6% in industrialized countries. Viral hepatitis B and C cause cancer of the liver; human papillomavirus infection causes cervical cancer; the bacterium Helicobacter pylori increases the risk of stomach cancer.
Environmental pollution
Environmental pollution of air, water and soil with carcinogenic chemicals accounts for 1 4% of all cancers (IARC/WHO, 2003). Exposure to carcinogenic chemicals in the environment can occur through drinking water or pollution of indoor and ambient air.
Occupational carcinogens
More than 40 agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances in the working environment are carcinogenic to humans and are classified as occupational carcinogens. These are causally related to cancer of the lung, bladder, larynx and skin, leukaemia, and nasopharyngeal cancer is well documented. Mesothelioma (cancer of the outer lining of the lung or chest cavity) is to a large extent caused by work-related exposure to asbestos.
Radiation
Ionizing radiation is carcinogenic to humans. Knowledgeon radiation risk has been mainly acquired from epidemiological studies of the Japanese A-bomb survivors as well as from studies of medical and occupational radiation exposure cohorts. Ionizing radiation can induce leukaemia and a number of solid tumours, with higher risks at a young age at exposure.
Residential exposure to radon gas from soil and building materials is estimated to cause between 3% and 14% of all lung cancers, making it the second cause of lung cancer after tobacco smoke. Radon levels in homes can be reduced by improving the ventilation and sealing floors and walls. Ionizing radiation is an essential diagnostic and therapeutic tool. To guarantee that benefits exceed potential radiation risks, radiological medical procedures should be appropriately prescribed and properly performed, to reduce unnecessary radiation doses, particularly in children.
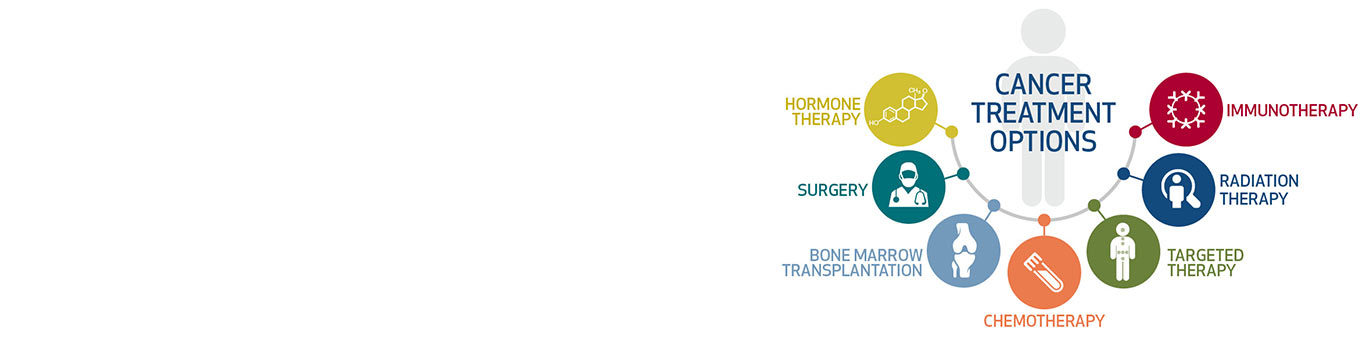
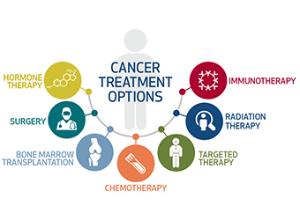
Treatment:
Bone Marrow/Stem Cell Transplantation
A stem cell transplant (sometimes called a bone marrow transplant) replaces diseased bone marrow with highly specialized stem cells that develop into the healthy bone marrow.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancer cells.
Immunotherapy and Vaccines
Immunotherapy and vaccines are a type of cancer treatments that use the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Personalized and Targeted Therapies
Personalized or targeted therapies are a type of treatment that targetsa cancer’s specific genes, proteins, or the tissue environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy x-rays or other particles to kill cancer cells.
Surgery
Surgery (the removal of cancerous tissue from the body) is the oldest type of cancer therapy.
When to Call the Doctor during Cancer Treatment
Find out which side effects from cancer and cancer treatment require immediate attention from your healthcare team and how to recognize them.
Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on preventing, managing, and relieving the symptoms of cancer and the side effects of cancer treatment.
Cost of treatment:
“It is a myth that cancer is just a health issue,” says the World Cancer Day website run by the Union for International Cancer Control. “Cancer negatively impacts families’ ability to earn an income, with high treatment costs pushing them further into poverty.”
With very little by way of government or insurance-sponsored healthcare, it is estimated that nearly 39 million Indians are pushed into poverty by all sorts of healthcare costs. With cancer, that is not difficult to imagine.
According to a July 2011 paper, by the Indian Statistical Institute, the average cost of cancer care in private hospitals can range between Rs 7 to 15 lakhs.
The treatment runs for at least one year. Hence, one year’s loss of income should also be considered. That is why it is essential to have critical illness plan to cover a cost of treatment. While your health insurance plan will cover minor injuries and illnesses a critical illness plan sufficiently covers medical expenses and the loss of income. Since the cost involved in the treatment of a critical illness is high, the sum assured provided by these plans are also as high as Rs 1 crore. A critical illness plan provides a lump sum amount on the diagnosis itself and one doesn’t have to wait to provide hospitalization bills, etc. Another major benefit of a critical illness plan is that it covers loss of income. You may not be in a position to earn or your income may be nominal because recovering from a critical illness may take few months and for those fewmonths you may be on a break from work. The lump sum amount you receive can be utilized the way you want to use it. For example, paying EMIs, child’s education, cost involved in advanced treatment like physiotherapy etc. can be managed if you have acritical illness plan.